Working agile has a lot of advantages. For one, it is attractive to the so sought-after newest generation of employees. But one side effect of it seems to be that it gets harder and harder to retain the employees for more than a couple of years. I see this in my everyday practice as a consultant in agile environments. It helps a lot, however, if the employer give room for development of talent instead of expecting people to fit the mold of the job description in all aspects.
Three reasons why agile employers should focus more on unique talents than the job description:
- The team results will be better
- People make the difference when they do what they love, are enthusiastic about and excel in
- People do not make their most impact while trying to get better at their weak points from the job description
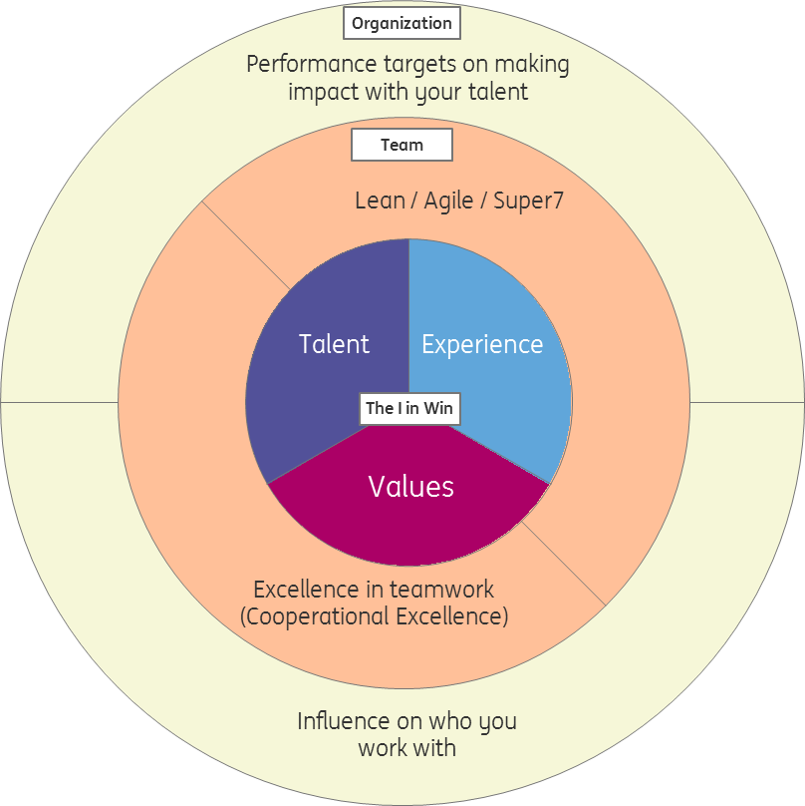
- Within an Agile working environment, people are working in teams
- Teams can optimize the workload in such way that each member uses their unique talent as much as possible, while making sure that every bit of the job gets done (cooperational excellence!)
- Helping employees to discover their unique talents will pay off in a big way – the whole team will perform better!
- Employees get more energy and enjoyment from the job
- Doing what you love to do while making it look easy – everyone would love to work like that every day
- To achieve this, one must know her/his own talents and how those can be applied within the job
- Employers should actively stimulate employees to discover their unique talents and help them understand in which aspects of the job those talents will shine
- Employees will find the job challenging and exciting for a longer period of time
- After the first year or so your employees will know their own talent and how to use it in the job
- The challenge and room for personal growth will then shift towards cooperating with the other team members
- Acknowledging the talent of others sometimes requires that you accept and recognize that you yourself can’t that at that high level – even if it is part of your job description
- Cooperation with different talents form your own requires empathy and genuine interest in the people you work with
- Personal growth comes from daring to be vulnerable in cooperation with others
- A strong team with lots of room for personal growth will keep your employees longer on board
Recently, I’ve had the privilege to work at an agile-working fintech scale-up. A very inspiring environment, but even here I saw that strong growth had shifted the emphasis somewhat from entrepreneurial ‘hands-on’ and ‘let’s see what works’ to ‘do your job’. Just a slight change in style of management makes all the difference in bringing back the fun of experimenting and giving room for talent. I will share some of my experiences in one of my next blogs.