Kata, Kaizen, DMAIC and Value Stream Re-Design – all Lean improvement methods can be used for Continuous Improvement for Agile and Super7 teams. But what is the best? Which method should we use? This is not an easy question. It depends. It depends on the scale of the desired improvement. It depends on the desired speed of improvement. And, some methods require more specific expertise than others.
Super7’s and Agile teams are faced with the question of which improvement method they should use for Continuous Improvement. They are expected to improve autonomously. Therefore, autonomous teams such as Super7 teams and Agile Teams should know these Lean improvement methods, enough to select the right one for the right problem.
A quick overview of the methods for Continuous Improvement for Agile and Super7
- Improvement of the entire value stream – the end-to-end process from demand to supply
- Re-design based on principles, most often the Lean Principles of Pull and Flow
- Uses Value Stream Mapping, a standardized way of visualizing how value flows
- Large improvements, with often quite extensive impact on people, processes and organization
- Requires expertise on Value Stream Mapping and Lean
- Lean Six Sigma improvement project approach
- Standardized phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control
- Fact based, measurement based problem solving by eliminating root causes
- Useful when the root cause of a problem is unknown
- Requires expertise on statistics, analytics and Lean Six Sigma at Blackbelt level
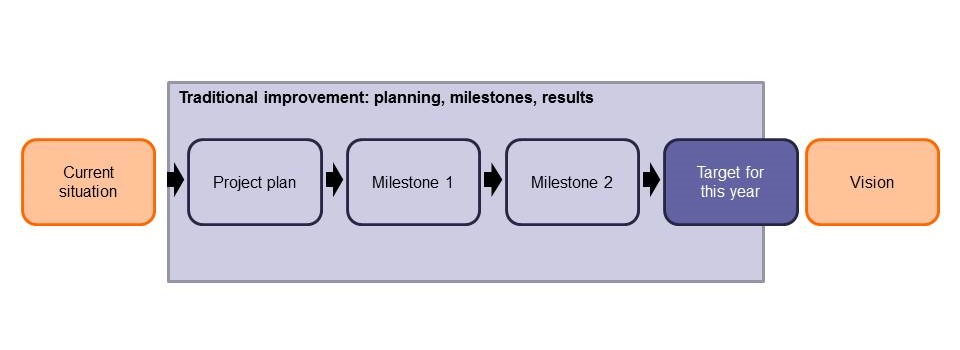
- Lean method for small step improvement in one or two days
- Quick analysis based on available data
- Improvement based on Lean principles
- Team of experts and operational employees
- Participants are made free from their regular work during the kaizen
- Sometimes facilitated by Blackbelts or Greenbelts
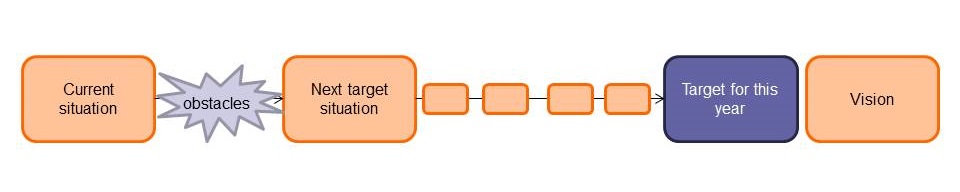
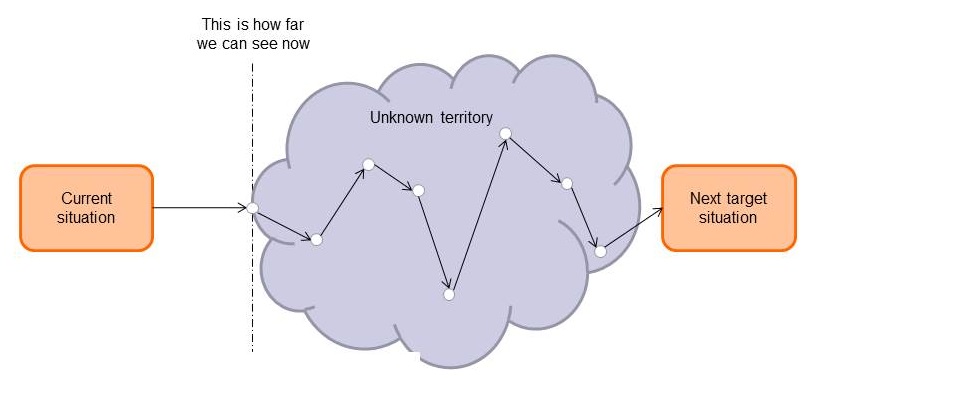
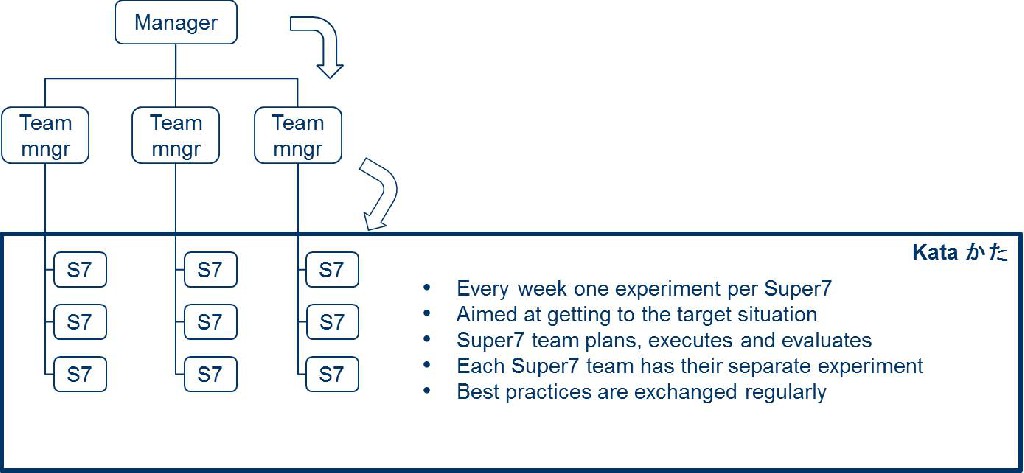
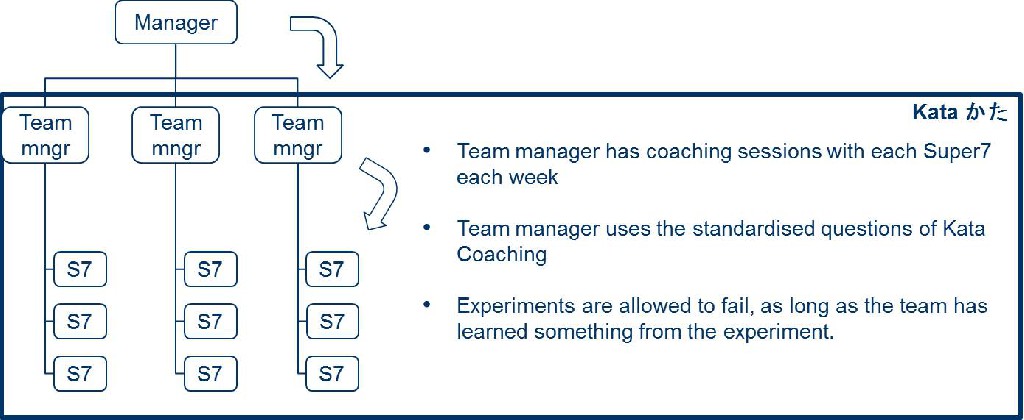
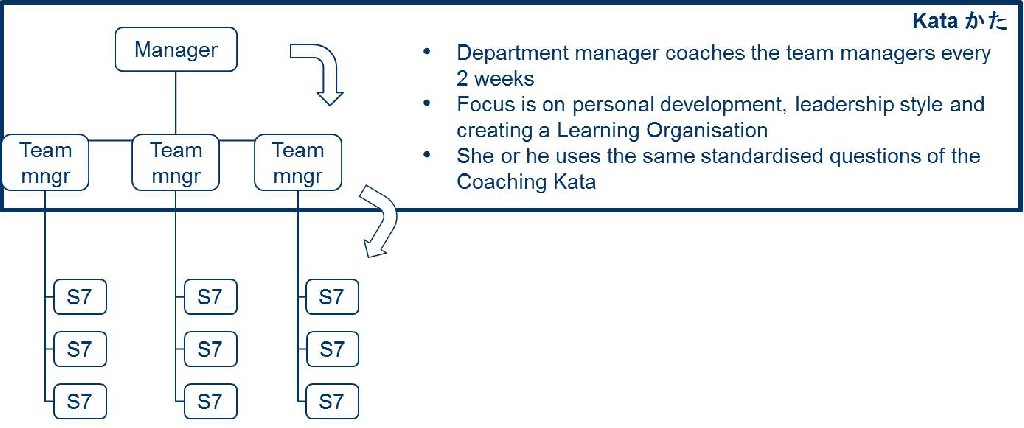
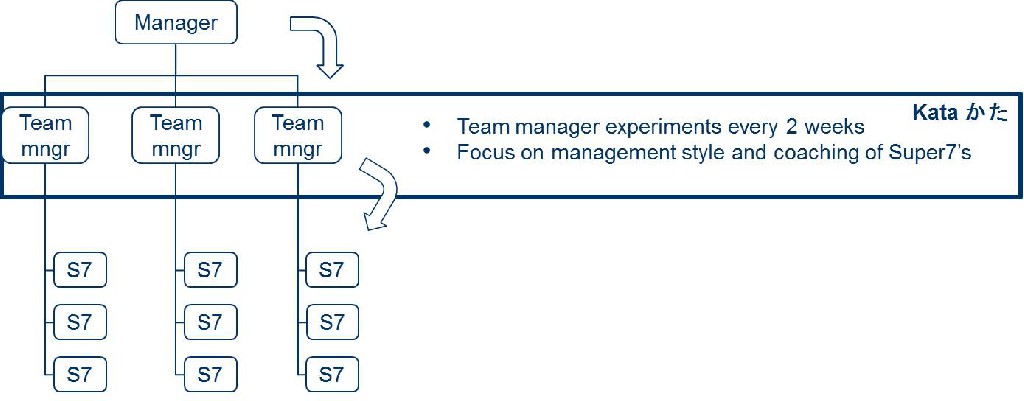
- Continuous improvement as a habit
- Every day, everyone, the way of the learning organization
- Many small experiments
- Discovering the way towards improvement as you go
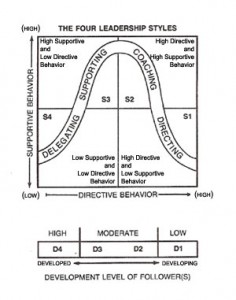
- Often supported with the use of Coaching Kata
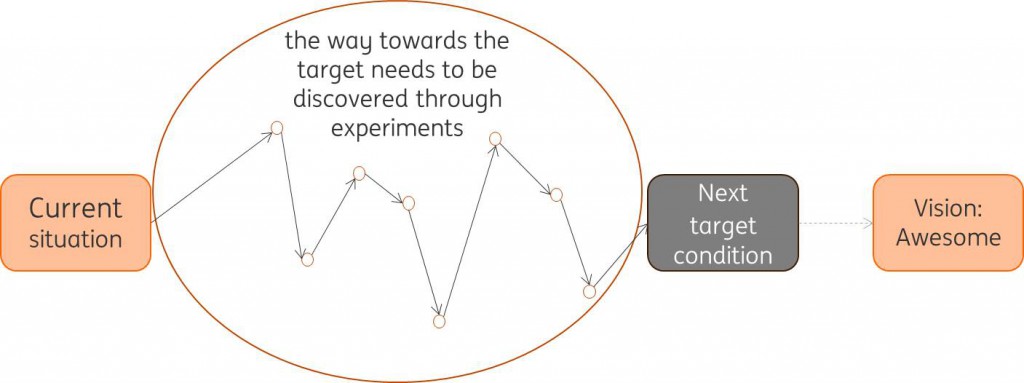
Improvement Kata
On earlier posts on this site (www.cooperationalexcellence.nl) you can find more information on this subject. For instance, how Improvement Kata is applied by Super7 Teams.
Menno R. van Dijk.