Leaders of developing autonomous teams can use the Situational Leadership theory to help and support the teams in their growth towards autonomy. Autonomous teams – Super7’s, Agile Squads, Scrum Teams, etc., can’t be fully autonomous from day one. So, how does a manager manage an autonomous team or Super7 that is still developing towards true autonomy? The answer: apply Situational Leadership.
Situational Leadership is based on the Hersey Blanchard Leadership Style matrix (see figure).
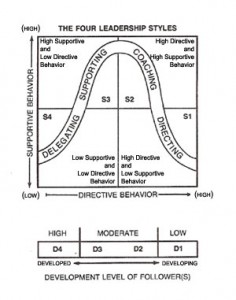
leadership styles for autonomous teams
A newly formed not-yet-autonomous team benefits from the directing leadership style. For instance, an Agile Squad in this phase needs to be told how to work the agile way. And the operations team manager of an immature Super7 team may need to tell the team to use their team board for daily planning.
As the autonomous team develops, the required leadership style changes accordingly. From Directing to Coaching, then on to Supporing and finally Delegating.
In practice, however, this can be quite challenging for a team manager. In my experience with Super7 Operations, the most difficult part of the implementation of Super7 is often to apply the right management style at the right time. And, every manager has his or her preferred style: the style that he or she does best. In a traditional operations department where managers steer on input and use strict quantitative controls, directing and coaching are most often needed. In a mature Super7 organization, however, Delegating and Supporting are the most useful styles.
As a result, the managers that are good at Directing and Coaching often make the most progress at the start of the implementation. But in the long run, a Super7 Operations department thrives under managers that are good at Delegating and Supporting. This asks a lot from the managers. It is good to acknowledge this fact. A successful implementation needs to address not only the methodological side of Super7 , but also take into account the ‘warm undercurrent’ of the change on a personal level.
Menno R. van Dijk.










