Super7 teams benefit from having the standard processing times and performance dashboards in place. These elements from Operational Management help a Super7 team in steering itself. When these basic elements from Operational Management are missing, implementation projects tend to take more time. It takes longer before the Super7 teams become autonomous.
Super7 Operations claims to be the next step for Lean in financial services. But how much does it owe to the previous Lean wave in financial Services? Which elements from Lean Operational Management are essential for the success of Super7 Operations?

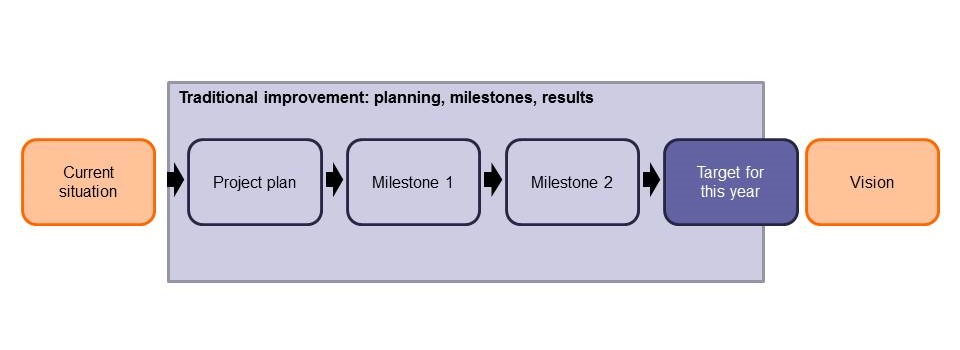
The way I see it, Super7 Operations is the logical next step for Lean in financial services. The first lean waves in financial services were often aimed at introducing standardized work, standard processing times, and making performance visible in performance dashboards.
Standard processing times make the work plannable. In Lean Operational Management, managers use them to plan the work for their teams. And afterwards, actual production is compared with planned production to calculate performance*. The manager then retains control through performance dashboards.
As I explain in my book, Super7 teams are steered on output. And, in Super7 Operations, the teams get the freedom and responsibility to plan their own work. However, both output steering and planning your own work becomes much easier when standard working times and dashboards are in place.
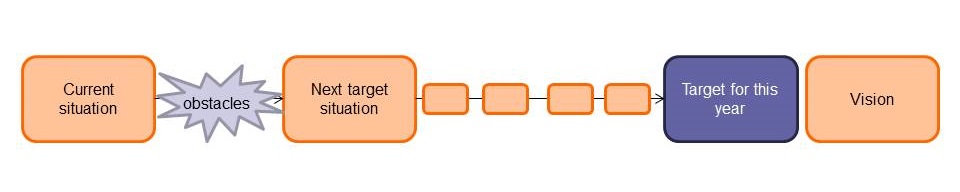
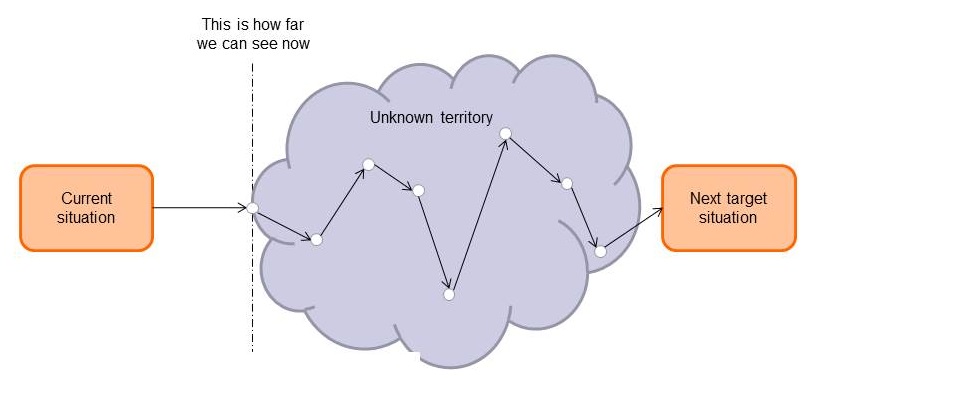
In Super7 Operations, the customer determines what needs to be done: the workload is based on the actual demand from that day. The manager sets the boundary conditions: that all requests are processed the same day (Today In, Today Out, or TITO). Work is often planned on forecast. But, to make planning decisions, the team needs to be able to match the forecasted workload to their planned capacity. And this can only be done when the forecasted number of customer requests can be translated into hours of work with the help of standard processing times.
Dashboards are equally important in Super7 Operations, but primarily for the teams themselves. They need to be able to see if all their Continuous Improvement efforts are paying off. And dashboards can be used to constantly raise the bar, both by the team itself and by the manager. Too many green lights become a red light, as the saying goes. This means that when the daily targets are met every day, this should lead to a more challenging target. More service in the same time for instance, or doing the same work with less capacity.
When standard processing times and performance dashboards, two basic elements from Lean Operational Management, are missing, implementation projects tend to take more time. It takes longer before the Super7 teams can make the decisions that make them truly autonomous.
Menno R. van Dijk
*Performance in Financial Services is often expressed in Total Team Effectiveness, a derivative of Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) which is the standard within manufacturing.